Supply and Demand Explained
I love coffee. Specifically, a cup of of hot black coffee in the morning with only the freshest ground roasted beans brewed at home. So, what does this have to do with economics?
Key Takeaways
The law of demand states that at a higher price consumers will demand a lower quantity of a good.1
The law of supply states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity of goods or services that suppliers offer will increase, and vice versa.2
The equilibrium price is the state in which market supply and demand balance each other, and as a result prices become stable.3
In this explanation, I’ll use my love for coffee to illustrate the economic theory that was popularized by Adam Smith in the year 1776.
Law of Demand
I go to the local coffee bean roaster and buy coffee beans. The lower the price, the more I'm inclined to buy maybe two bags instead of one. That's the law of demand. The lower the price, the more I demand.
Law of Supply
Now, let's say I'm a farmer, and I grow and sell coffee beans. For a seller, it's the opposite. The higher the price, the more coffee beans I want to supply and sell. Because the more money I can make, that's the law of supply. The higher the price, the more I supply.
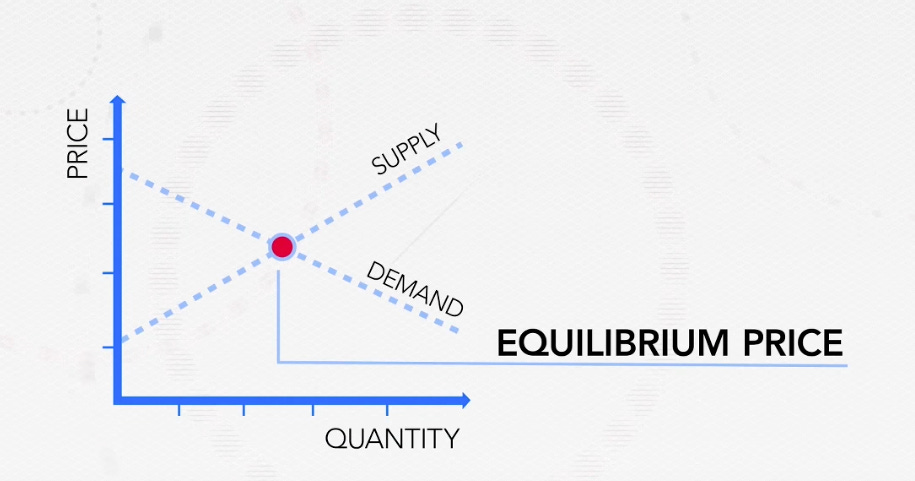
Equilibrium Price
Now, where these two lines intersect is our equilibrium price or market price. That's the price I pay to buy my coffee beans.
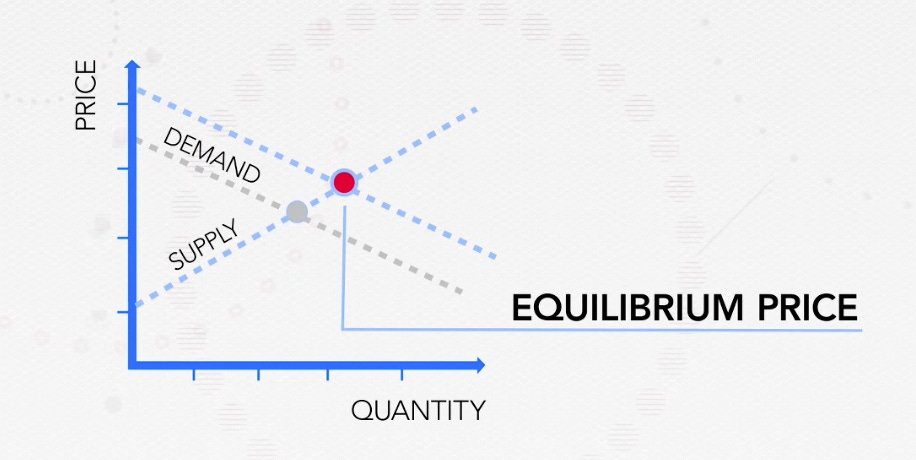
So far, simple, right? But here's where it gets really interesting. What if there's a new record that shows that drinking black coffee is even better for your health than you thought? Now at the same price, we want more coffee beans, so the demand has gone up. Now the entire curve shifts to the right, because at any price, people want more coffee than before.
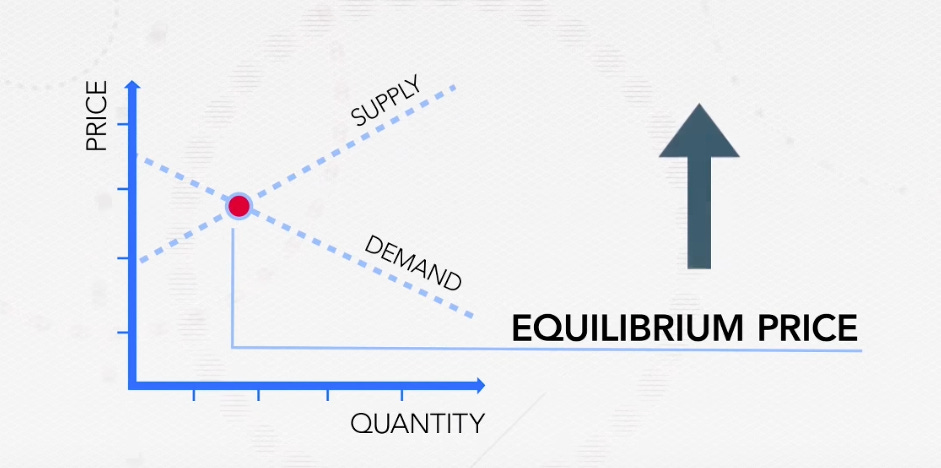
And, what if really bad weather destroys some of the coffee bean crop?
Now, at every price, farmers will supply less and the entire curve shifts to the left and the equilibrium price increases. So, now only the people who can afford really expensive coffee beans buy them.
The rest of us peasants switch to green tea.
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/l/lawofdemand.asp
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/l/lawofsupply.asp
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/equilibrium.asp